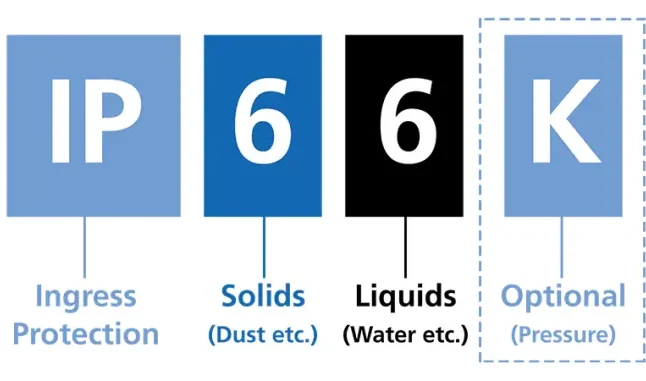
The use of explosion-proof equipment and instrumentation equipment is mandatory in high-risk industrial environments. The degree of protection IP is widely used in the production of industrial electrical equipment and includes two numbers that determine the degree of protection of electrical equipment against solid and liquid particles. The number on the right shows the amount of protection against liquid particles and the number on the left shows the amount of protection against solid particles.
What is the continuation of the degree of IP protection? We will answer.
What is the degree of IP protection?
The IP code is a system for classifying the degree of protection of electrical equipment. The degree of IP protection is defined by the international standard EN 60529 (British Standard BS EN 60529:1992). This is the standard used in most countries of the world, as it is mandatory for electrical and lighting products to indicate the degree of IP protection. In this way, the user can know whether the light or lamp he bought is suitable for installation in a certain environment (industrial environments or high-risk factories) or not.
The IP standard includes two numbers that determine the degree of protection of electrical equipment against solid and liquid particles. The number on the right shows the amount of protection against liquid particles and the number on the left shows the amount of protection against solid particles. The purpose of this standard is to provide users with more detailed information for protection and waterproofing.
What are the reasons for using IP protection degree?
Pollution introduced into electronic devices reduces the useful life and eventually causes the entire device to fail. Among these pollutions, we can mention dust, which can cause a lot of damage when it enters the electrical enclosure. Dust can collect in electrical outlets, ports, or gaps, and if the dust is excessive, it can cause heating of circuits and conduction.
Moisture is another thing that can have negative effects on electrical equipment. Getting wet is another reason that causes electrical equipment to fail, and chemicals, especially cleaners, can have corrosive and destructive effects on electrical equipment.
Concepts of numbers next to IP protection degree
The IP standard consists of two numbers. These two numbers determine the degree of protection of electrical equipment against solid and liquid particles. The number on the right indicates the level of protection of the equipment against liquid particles and the number on the left indicates the level of protection of the equipment against solid particles. This standard was created in order to provide more accurate information to users for the protection and waterproofness of the equipment, and one of its very important applications is in explosion-proof electrical equipment used in high-risk environments.
The first number: Protection of solid particles
The first number in the IP standard is between 0 and 6, which indicates the degree of protection against hard foreign objects and protection of people against contact with live parts.
This number indicates the protection of the device against the penetration of foreign objects such as dust, tools, fingers (to prevent electric shock), insects, etc.
| Prime number | Description | Protection rate |
|---|---|---|
| X | _ | X means that there are no data to determine the degree of protection according to these criteria. |
| 0 | No foreign body safety | Without any protection against contact and entry of objects |
| 1 | Immunity against foreign object larger than 50 mm | Protection against any large body surface |
| 2 | Immunity against foreign object larger than 12 mm | Protection against fingers or similar objects |
| 3 | Immunity against foreign object larger than 2.5 mm | Protection against thick wires, tools and… |
| 4 | Immunity against foreign body larger than 1 mm | Protection against most wires, narrow screws, large ants and… |
| 5 | Safety against sediment and dust | In case of dust and sediments entering, the work of the equipment will be disturbed. |
| 6 | Safety against dust penetration | Full protection against contact (anti-dust) no dust ingress |
The second number: Protection of liquid particles
The second figure shows the level of protection against the harmful entry of liquid particles and the way of spraying these particles is very effective. If a device is IPX7 (water submersion rated), it is not necessarily IPX4 (splash protected). A device with both IP standards is shown separately by indicating its origin (eg IPX4/IPX7).
| The second number | Description | Degree of protection |
|---|---|---|
| X | _ | X means that there are no data to determine the degree of protection according to these criteria. |
| 0 | Lack of protection against water penetration | Lack of protection against water penetration |
| 1 | Safety against vertical drops of water | Test duration: 10 minutes Water equivalent to 1 mm (0.039 inches) as precipitation per minute |
| 2 | Safety against water falling at an angle of 15°C compared to vertical | Test duration: 10 minutes Water that is equivalent to 3 mm of rain per minute. |
| 3 | Safety against spreading or spraying water up to an angle of 60 degrees Celsius | Test duration: 5 minutes Water volume: 0.7 liters per minute Water pressure: 80–100 kPa |
| 4 | Safety against splashing water from any direction | Test duration: 10 minutes in all directions Water volume: 10 liters per minute Water pressure: 80-100 kilopascals |
| 5 | Safety against water spray by the nozzle in all directions | Test duration: 1 minute per square meter Water volume: 12.5 liters per minute Water pressure: 30 kPa at a distance of 3 meters |
| 6 | Safety against high pressure water flow | Test duration: 1 minute per square meter Water volume: 100 liters per minute Water pressure: 100 kPa from a distance of 3 meters |
| 7 | Safety against high pressure water immersion | Test duration: 30 minutes When the equipment compartment is immersed in water under certain pressure conditions and time (maximum 1 meter). |
| 8 | Safety against submersion or complete submersion in water | Test duration: continuous immersion in water Determined depth: determined by the manufacturer (usually up to 3 meters). |
Electrical devices that have a high degree of protection are usually used in dangerous environments that are prone to explosion due to the presence of flammable gases and vapors. This type of equipment is called explosion-proof equipment.
Examples of IP protection in electrical equipment
- IP68 means: Impermeable to dust – Full protection against immersion in water
- IP41 means: Complete protection against tools and wires with a diameter greater than 1 mm – Full protection against water dripping from raindrops
- IP66 means: The first number 6 means that the equipment is impervious to dust – The second number 6 means that the equipment is safe against high pressure water flow
- IP 57 means: The number 5 means that the equipment is safe against sediment and dust – The number 7 means that the equipment is safe against immersion in water with high pressure
- IP67 means: Complete protection against very small objects such as dust – Full protection against immersion in water up to 1 meter deep
- IP43 means: The number 4 means that the equipment is safe against most wires, narrow screws, large ants, etc. – The number 3 means that the equipment is safe against spreading or spraying water up to an angle of 60 degrees Celsius